Hearing loss is a more common issue than you might think
According to the World Health Organization, hearing loss is diagnosed when a person is unable to hear as well as someone with normal hearing, which is usually a hearing threshold of 20 dB or better in both ears. Many people may not even realize they have hearing loss, as it develops gradually over time and can take a while to become severe enough to seek treatment.
Believe it or not, about 48 million Americans experience hearing loss, and each individual experience can differ from person to person. There are actually four different types of hearing loss, and each is caused by different things and treated differently, depending on the case.
Read on to learn more about the different types of hearing loss, the causes of each, and how each is uniquely diagnosed and treated.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss is the most common and most easily treated type of hearing loss, as it’s caused by something stopping sounds from passing through the outer or middle ear. This can be caused by a lot of different things, including fluid in the middle ear (from allergies or sickness), a buildup of ear wax, an ear infection, or even a hole in your eardrum.
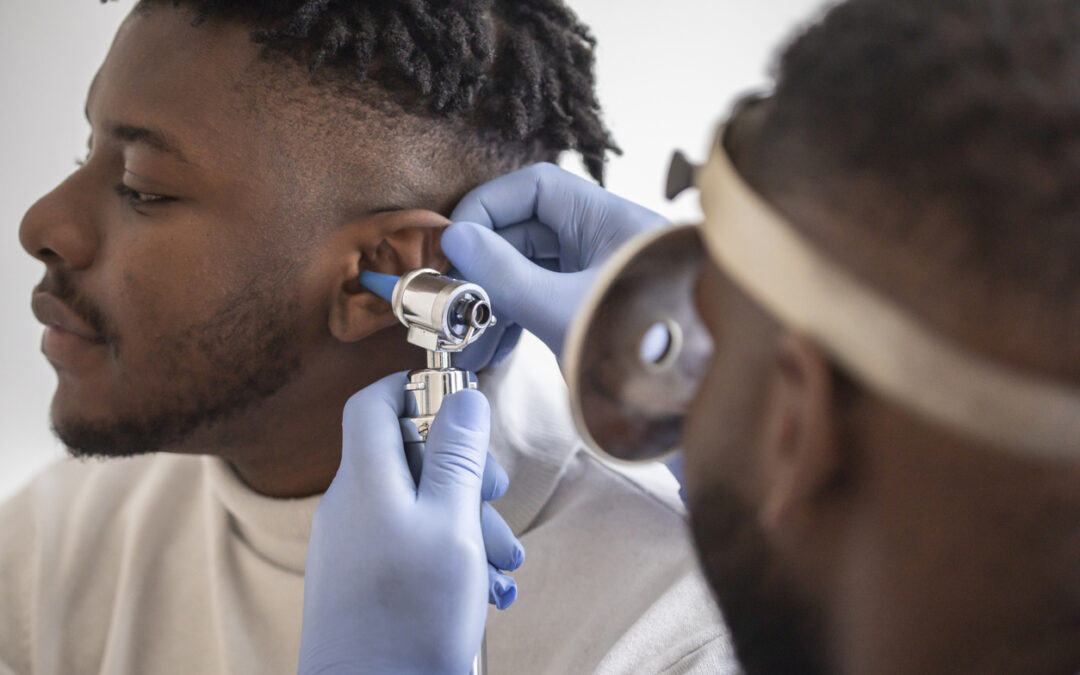
To diagnose conductive hearing loss, a doctor will probably conduct a hearing test and do an ear exam. Depending on the severity and exact cause, this type of hearing loss is often treated with medicine (in the case of an infection) or surgery (in the case of more physical damage to the ear itself).
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is another fairly common type of hearing loss, and it’s caused when there’s an issue with or damage to the inner ear or hearing nerves that live in your inner ear. It’s most often caused by illness, genetics, certain drugs that are toxic to hearing, aging, or even consistent or repeated exposure to loud noise (also known as noise-induced hearing loss).
This type of hearing loss is best diagnosed by an audiologist or other hearing care provider through a hearing test and ear exam, and treatment very often includes hearing aids.
Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is exactly what it sounds like – some combination of conductive hearing loss and sensorineural hearing loss. You may have this specific type, for example, if you’ve had lots of exposure to loud noises through your profession and also suffer from seasonal allergies. Or, maybe you went a little too deep with a q-tip and also battled an illness that impaired your hearing. But, really anything that causes conductive or sensorineural hearing loss can also cause mixed hearing loss.
A hearing care specialist is the best person to help diagnose and treat mixed hearing loss, as they can conduct several tests and physically examine your ears to determine the main type of hearing loss present and the most effective treatment plan.
Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder
Finally, Auditory Neuropathy Spectrum Disorder is the type of hearing loss that is less about sound actually reaching the inner ear, like with other types of hearing loss we’ve already discussed, and more about your ear’s ability to process that sound and translate it into a form that the brain can understand and use. This disorder most often affects children, as it affects an individual right at birth and is diagnosed early in life.
Though it is rare and unlikely that you will develop this disorder as you age, a cochlear implant is a first-choice treatment for more intense cases, but hearing aids can often be a good enough treatment option for more mild cases.
–
While over 48 million Americans experience some form of hearing loss, only one in five people who could benefit from hearing aids actually uses them – that’s just 20% of the hearing impaired population!
If you’re ready to take control of your hearing loss or want to get a professional’s opinion on your hearing experience, schedule an appointment for a free hearing test with your local Beltone Tristate practice, and our team of friendly hearing care professionals will be happy to help.